We share and transfer knowledge and technology to the public, experts, politics, administration and the business world.
Joint Initiative for Research and Innovation (Pakt für Forschung und Innovation)
In 2005, the federal and state governments launched the Joint Initiative for Research and Innovation (Pakt für Forschung und Innovation, PFI), which has been updated several times since then, with the aim of strengthening the competitiveness of the German science system by making better use of existing potential.
Based on research policy goals, the funding agencies have established target agreements with the science organizations for the respective organization-specific implementation.
One of these goals is to strengthen transfer to industry and society: "An efficient science system is the breeding ground for innovations and provides knowledge for action and decision-making to meet major societal challenges. The science organizations will give central priority to the transfer and utilization of ideas, research results and knowledge through intensive exchange with industry, society and politics."
- Pakt für Forschung und Innovation - Update 2021-2030 (PFI IV): PDF file
- Helmholtz website: Joint Initiative for Research and Innovation
Field of action II "Strengthening transfer into science and society"
Strengthening transfer to industry and society is an important part of our mission. A central concern for the coming period of the Joint Initiative for Research and Innovation (2021-2030) will therefore be to anchor knowledge and technology transfer comprehensibly at all levels, in the Centers' Leitbilder and missions, and in the goals of the research fields.
Measures for the targeted expansion of knowledge transfer initiatives are:
Anchoring and strategies
- Anchoring the transfer of knowledge and technology as a fixed point of reference in the mission statements and missions of the centers ".
- Development or review of transfer strategies with regard to expansion in the area of technology transfer" in the area of technology transfer".
- Strategic focal points in the area of knowledge transfer and measures geared to these focal points
- Budget for transfer support and transfer projects
- Strengthening the culture of recognition ('transfer welcome')
- Further professionalization of technology transfer offices
- Anchoring transfer as part of research planning
- Improvement of transfer-related communication strategies
Spin-offs
- Number of invention disclosures
- Patents
- Spin-offs
- Validation funding - application for funding from the VIP+ federal program and other programs at federal and state level
Innovation Fund
- Use of funds for the promotion of innovation projects from center-internal Innovation Fund"
Partners for industry
- Establishment of new development partnerships with industry
- Contract research
- Advanced training for areas outside science / qualification offers for an activity in / cooperation with industry
- Establishment of digital platforms, Open Labs, Real Labs and Demo Labs
- Concepts for technology marketing
Knowledge transfer
- Information services
- Establishment of further professionalized units in the field of knowledge transfer
- Citizen dialogue and citizen science
- Scientific policy advice
- Standardization and norming
Actions & Activities of MTET Scientists
- Citizen Dialogue and Citizen Science
- Commissioned studies as a basis for political decisions (client: public authorities)
- Participation in procedures of recognized national organizations for standardization (DIN, ISO, CEN, DWA, ITVA)
- Strengthening of technology transfer at large research infrastructures
- Transfer to studies and teaching
- Patenting of research results
- Founding of startups & spin-offs
- Scientific collaborative projects for technology demonstration together with industry
Measures of the Helmholtz Association
The Helmholtz Association has several knowledge and technology transfer instruments. Each starts at different stage in the application-readiness level, in the progression from basic research to application, and each helps researchers bridge specific gaps in the transfer pathway.
Helmholtz website: Helmholtz Association Transfer Instruments

...is a KIT service unit and supports knowledge and technology transfer at KIT with several measures.
moreContents
sprungmarken_marker_1130

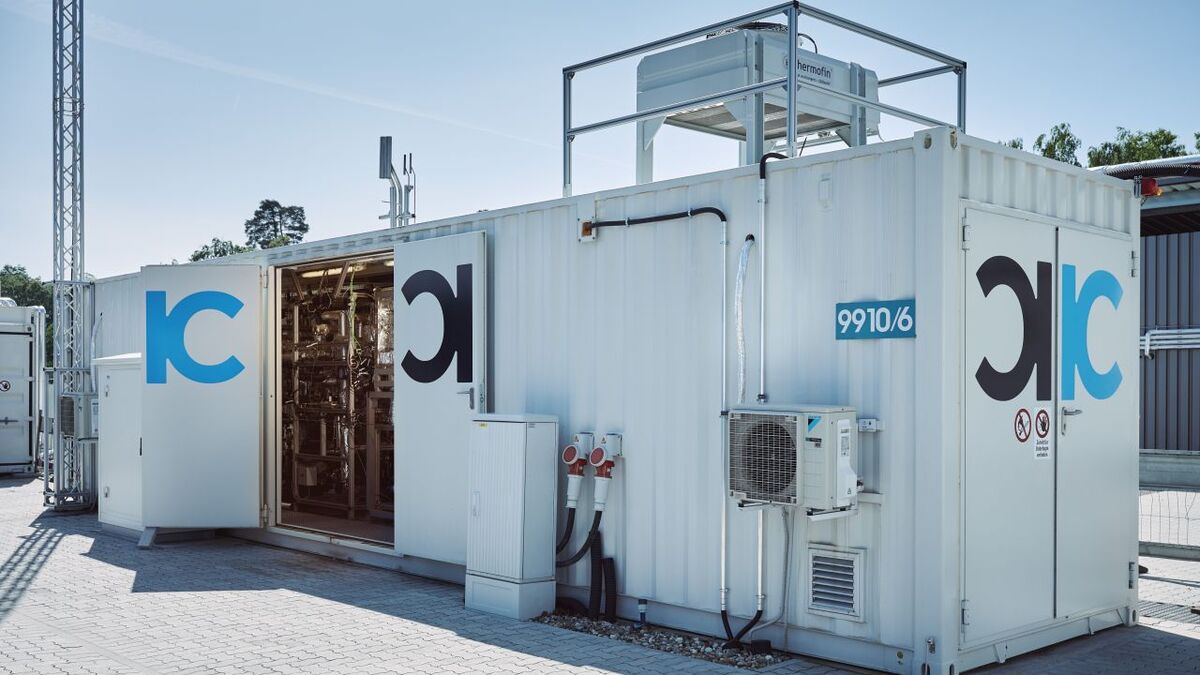
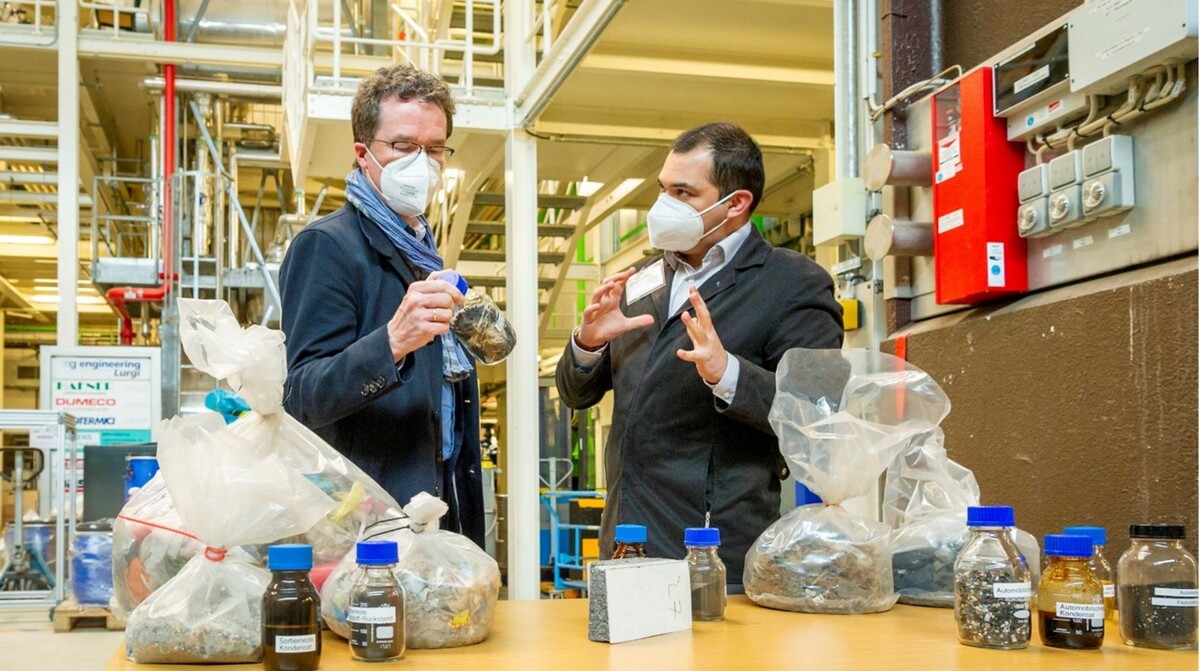
Germany‘s 1st chemical recycling plant for mixed plastic waste: Arcus Greencycling Technologies operates the scale-up of KIT’s screw reactor pyrolysis technology at Frankfurt Höchst supplying BASF with feedstock for syngas production and steam cracker
https://arcus-greencycling.com/en/
Sebastian Büchele (left, Litona founder) and Tom Bötticher show a bottle of Prussian white, an energy storage material for sodium-ion batteries. They can be produced using abundant and inexpensive materials reducing the dependence of Europe on imports of resources.
https://www.litona.de/
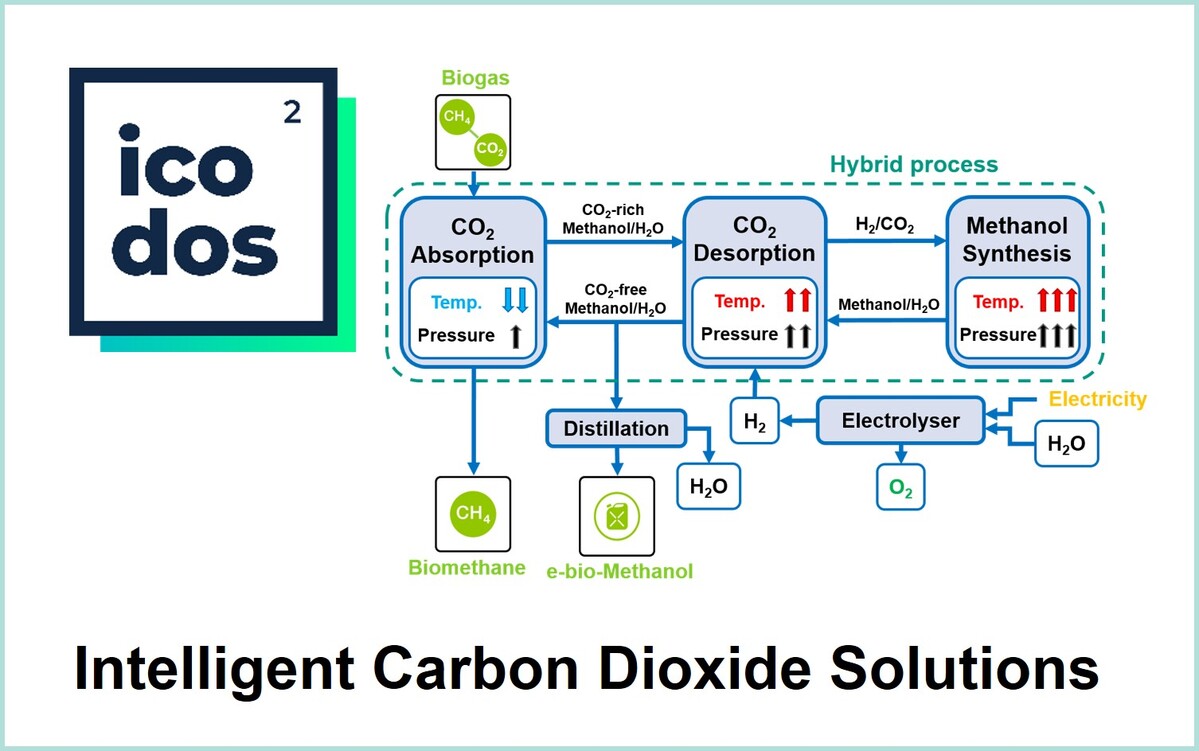
KIT`s startup ICODOS uses an innovative Power-to-X technology to produce green methanol. ICODOS, KIT, and BASF launch world’s first fully-integrated, automated and dynamically operated e-methanol plant.
https://icodos.com/
Prio Optics produces optical filters using a game-changing inkjet printing method; Breaking free from the limits of vacuum chambers, we enable customization, cost-effectiveness in small batches, sustainable production and address unanswered demands
https://www.prio-optics.com/
At varmo, we’re pioneering a new generation of heat flow sensor technology that enhances the way industries manage thermal processes. By integrating our innovative sensors into your products and systems, you can optimize efficiency, detect anomalies ...
https://www.varmo-sensors.de/
At REVYVE, we are passionate about pioneering innovation in the maritime sector. We firmly believe that hydrogen holds the potential to revolutionize the way we navigate the world's waterways. Join us on our journey to clean boating!
https://www.revyve.tech/
Phytonics GmbH was founded in 2021 out of the KIT. Phytonics develops optical coatings with a surface micro-texturing inspired by or replicated from plants. Its prime objective is to foster the generation of photovoltaic electric energy by offering cost...
https://phytonics.com/en/company/
Modular chemical plants for Gas-to-Liquid, Power-to-Gas & Power-to-Liquid processes producing CO2 neutral fuels for mobility, storage of "green" energy & decentralized production of chemicals: INERATEC
INERATEC GmbH
bioliq® process & exploitation concept was developed in cooperation with AirLiquid & Pricewaterhouse Coopers. R&D platform for refuels with automotive, chemical & petroleum industry.
bioliq® website
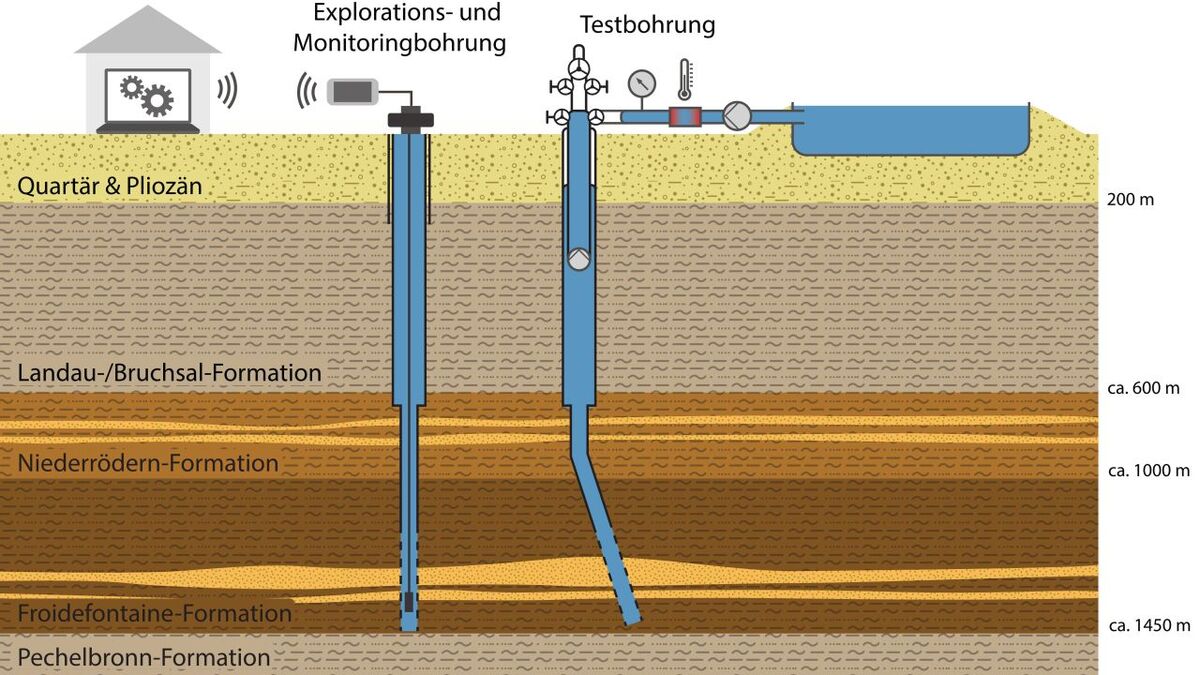
Utilization of GEothermics for a Climate-Neutral Heat Supply at KIT Campus North - Inter- and Transdisciplinary Co-Design of an Implementation COncept.
more
Prof. Helmut Ehrenberg was appointed by the Federal Ministry of Education & Research to the advisory board "Battery Research Germany" & joins as KIT's third MTET scientist.
more
The objective of the project is to identify key innovations of energy-efficient solutions and to network them in their different application areas within the BMWi Research Network Energy.
EE4InG website
Workshop of industry, science & policy makers about innovative products & technical solutions reducing energy consumption & CO2 emissions.
EE4InG websiteHannover Messe 2024 - Discover our contributions to sustinable materials and technologies for the energy transition
Highlights from the Technological Development
Come and visit us at the Future Hub > Hall2, Booth B35
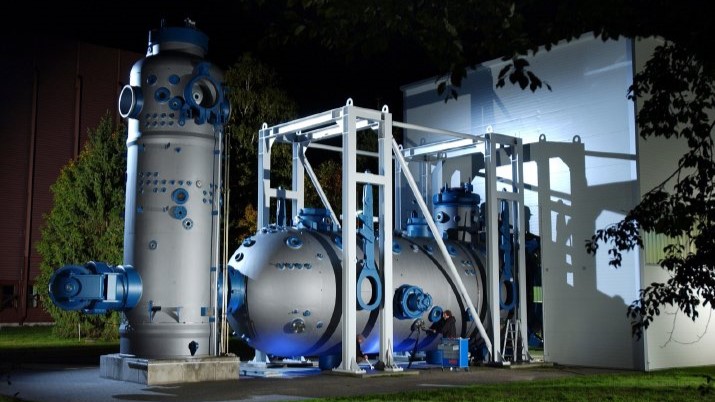
Net-Zero Circular Concrete – Concrete without Emissions Harmful to the Climate
An innovative circular approach is pursued to produce concrete with a low consumption of resources and without emissions affecting the climate. Concrete waste resulting from the demolition of buildings is crushed and sorted into coarse and fine fractions. Limestone is added to the fine fraction to produce a binder at moderate process temperatures. The coarse fraction absorbs the carbon dioxide (CO2) produced in the course of the process. Together with the binder, it is used for producing new concrete. The pilot plant that is being set up at KIT will be used to gain the know-how for the production of larger quantities.
By loading you accept YouTube's privacy policy.
Come and visit us at the Energy Solutions > Hall13, Booth C76
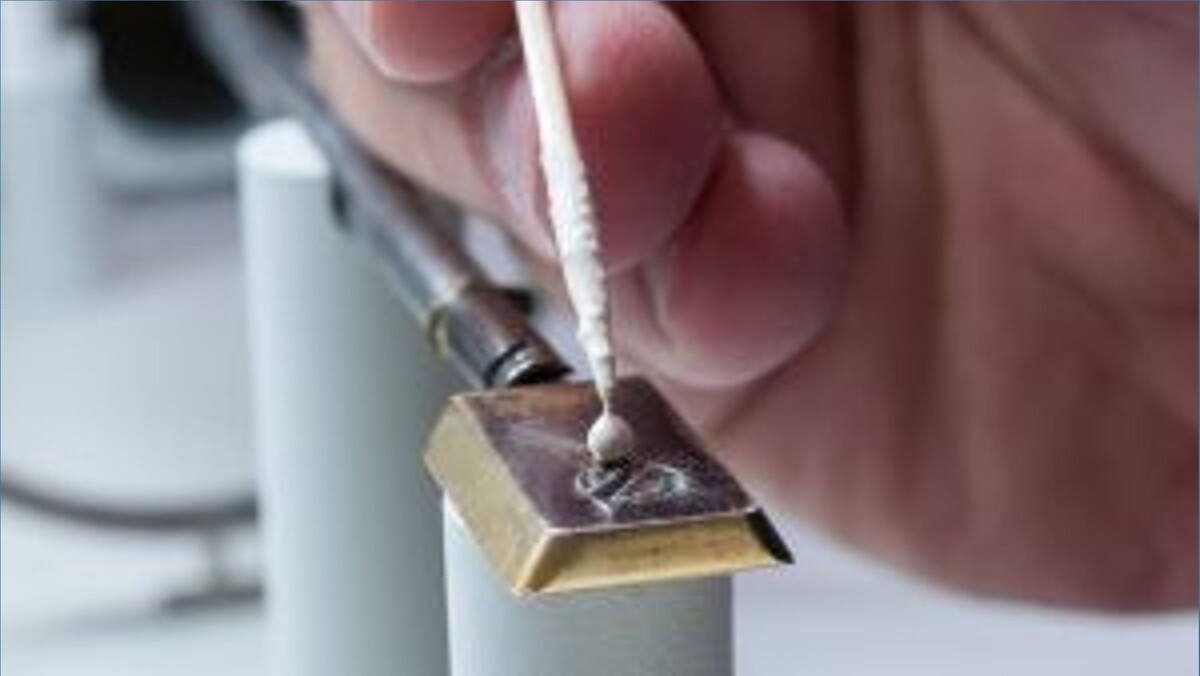
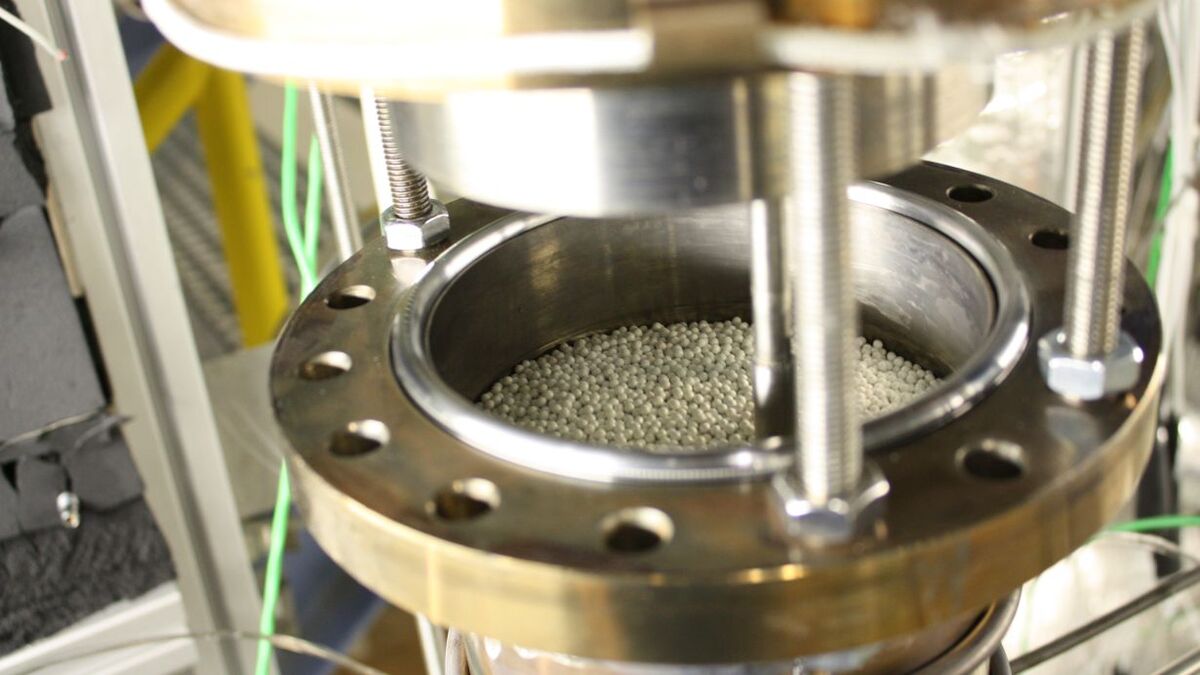
Heat Transfer with Liquid Metals
Thermal energy storage systems can store energy in the form of heat as needed by industrial high-temperature processes in chemical or metal processing industries. Liquid metals enable heat storage at very high temperatures. They are combined with ceramic beads having a high storage density and long-term storage capacity. A pilot plant will demonstrate operation of a liquid metal-based heat storage system.
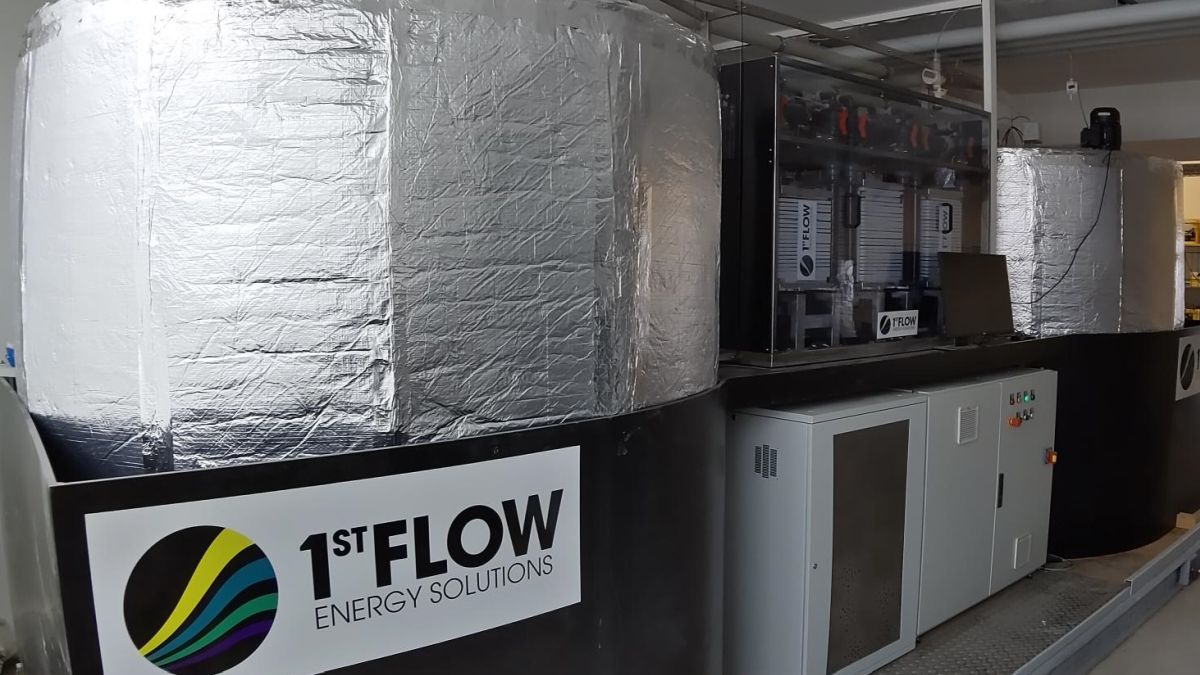
BiFlow – Hybrid Storage System for Power and Heat Supply
The energy transition and extended use of renewable energy sources require large storage capacities. The BiFlow project focuses on the development of a hybrid storage system that combines specific advantages of the lithium-ion battery with those of the redox-flow battery. The electrolyte tanks of the redox-flow battery are additionally used to store heat. In connection with a thermal coupling module, it increases the storage capacity and total efficiency of the system. This opens up new options for cost- and space-efficient co-storage.
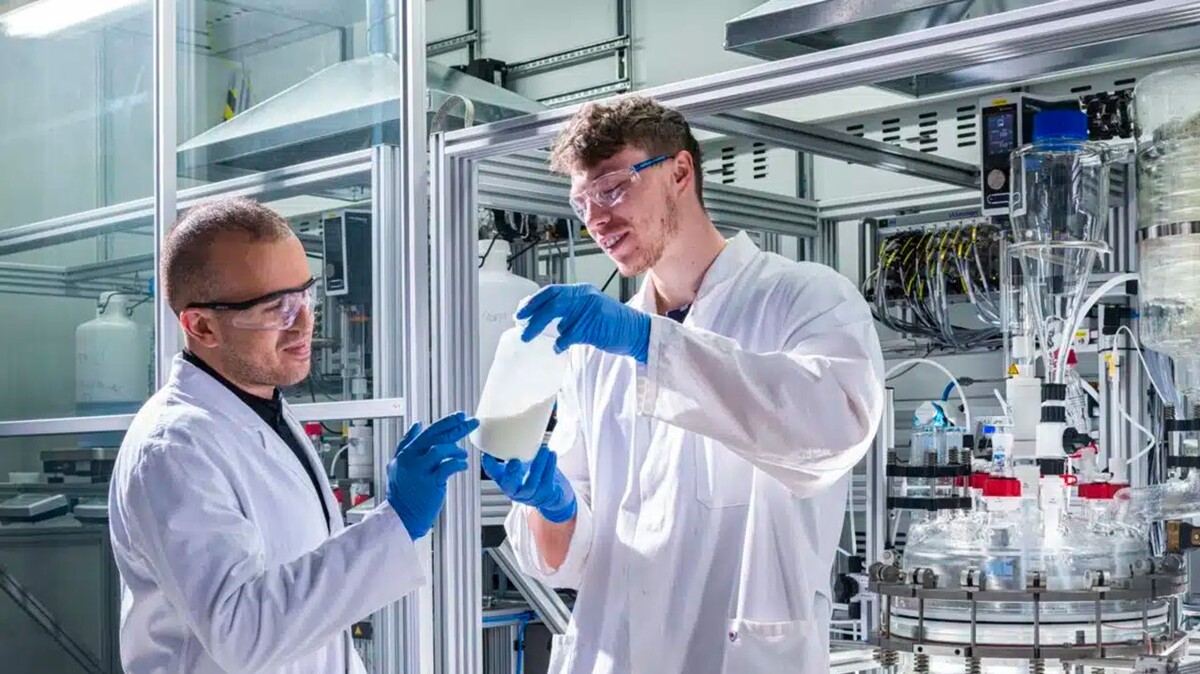
Litona – Materials for Sustainable Sodium-ion Batteries
KIT’s startup Litona develops energy storage materials for sodium-ion batteries. Sodium-based batteries can be produced using abundant and inexpensive materials. This will reduce future costs of batteries and the dependence of Europe on imports of resources. Litona’s work presently concentrates on Prussian white analogs. These storage materials are of interest for stationary energy storage applications and for the e-mobility sector.
By loading you accept YouTube's privacy policy.
Safe Hydrogen Storage Systems
Hydrogen (H2) is a clean, efficient, and reliable energy carrier for many applications. KIT has more than 30 years of experience in H2 safety research. Its hydrogen test center HYKA accommodates worldwide unique infrastructures for experiments covering various release and combustion scenarios. The PET (partially vented explosion tube) is used to study turbulent combustion processes in hydrogen-air mixtures found in partially vented geometries. These may be leaky H2 storage tanks in rooms with doors and windows. Researchers also develop 3D simulation programs to specifically analyze and improve safety conditions.
KIT at Other Stands
The Center for Electrochemical Energy Storage Ulm & Karlsruhe (CELEST) will also be present at the stand of Baden-Württemberg international (hall 12, stand D15). KIT, Ulm University, and the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg (ZSW) cooperate in CELEST, the biggest platform for electrochemical storage systems in Germany.
At the stand of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (hall 2, stand A28), the AppLHy! exhibit highlights the design and implementation of a combined transport route for liquid hydrogen and electric power. Power will be transmitted with the help of high-temperature superconductors. Read more.
KIT’s Contributions to the Conference Program
Tech Transfer Conference Stage (Hall 2, Stand B02)
Tuesday, April 23 2024, 14.50 hrs
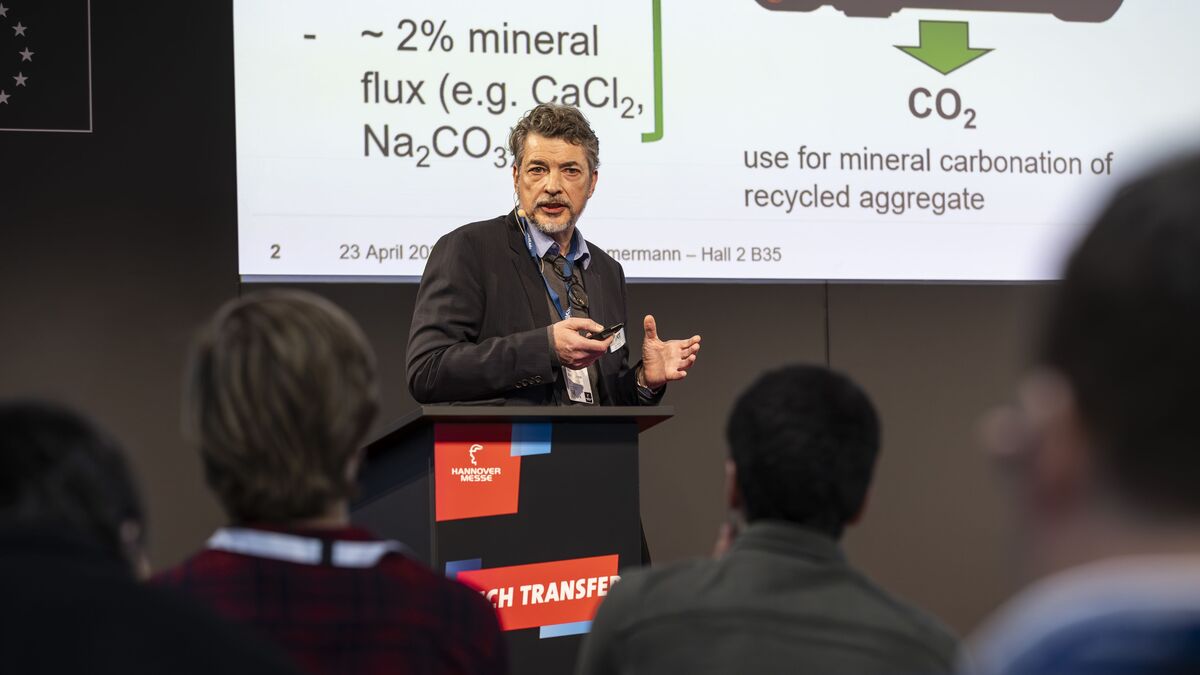
Presentation in English with live interpretation: Net-zero Circular Concrete
Dr. Peter Stemmermann, Institute for Technical Chemistry of KIT.
ENERGY 4.0 Academy (Hall 12, Stand D35/26)
Thursday, April 25, 2024, 10.00 hrs
Presentation in German: Methane pyrolysis as a key element for emission-free hydrogen and carbon production
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Thomas Wetzel, Institute of Thermal Process Engineering of KIT
lookKIT 2024/1: Ressources. Circular Economy. Energy.
source: PDF
Global resource consumption is increasing rapidly. According to calculations, we would have needed significantly more than one earth to meet demand two years ago. This emphasizes that we need to use materials and energy more carefully and efficiently. Therefore circular economy and intelligent storage technologies are important keywords At the Hannover Messe, KIT researchers present solutions to this problem.
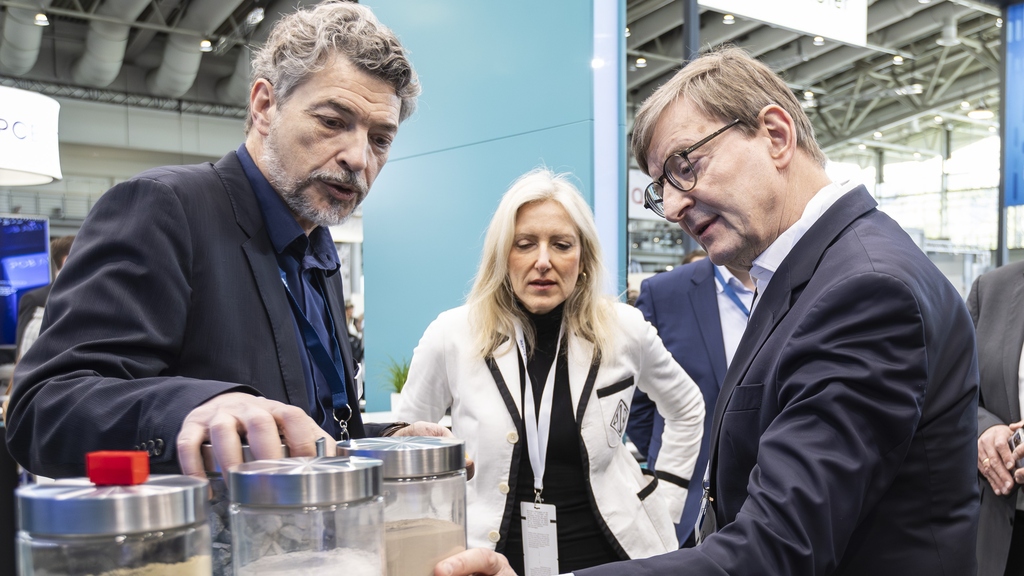

Dr. Peter Stemmermann, left, Institute for Technical Chemistry, KIT in discussion with Helmholtz President Prof. Dr. Otmar D. Wiestler and Franziska Broer, Managing Director of the Helmholtz Association about Net-Zero Circular Concrete - concrete without climate-damaging emissions.

Sebastian Büchele (left, Litona founder) and Tom Bötticher show a bottle of Prussian white, an energy storage material for sodium-ion batteries. They can be produced using abundant and inexpensive materials reducing the dependence of Europe on imports of resources.
https://www.litona.de/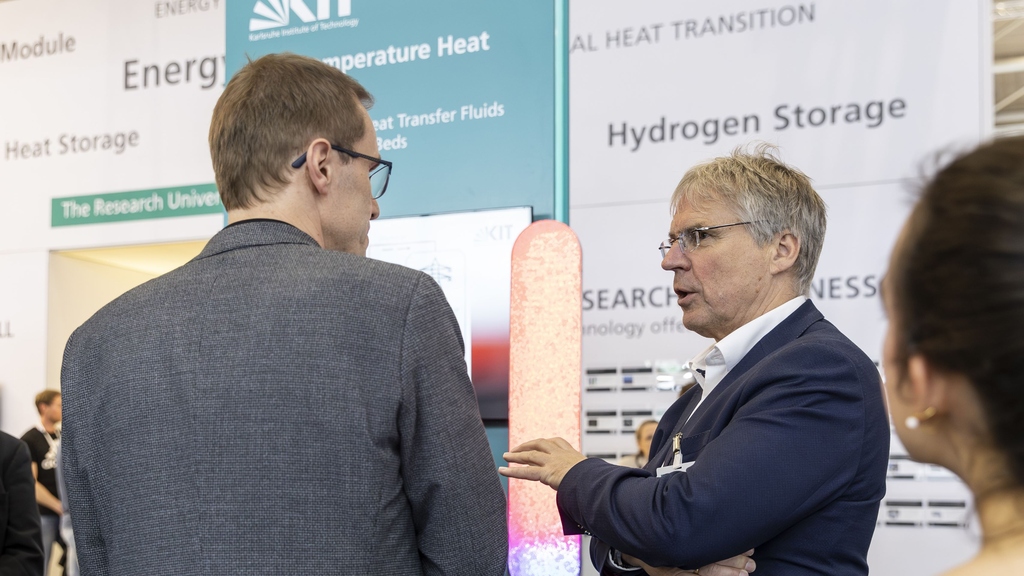
Prof. Holger Hanselka, Fraunhofer President and Prof. Thomas Wetzel, KArlsruhe Liquid metal LAboratory (KALLA), KIT, discuss the first pilot plant demonstrating operation of a liquid metal-based heat storage system.
Discover the MTET Contributions @Hannover Messe 2023!
Energy Solutions
Hall 13, Booth C70
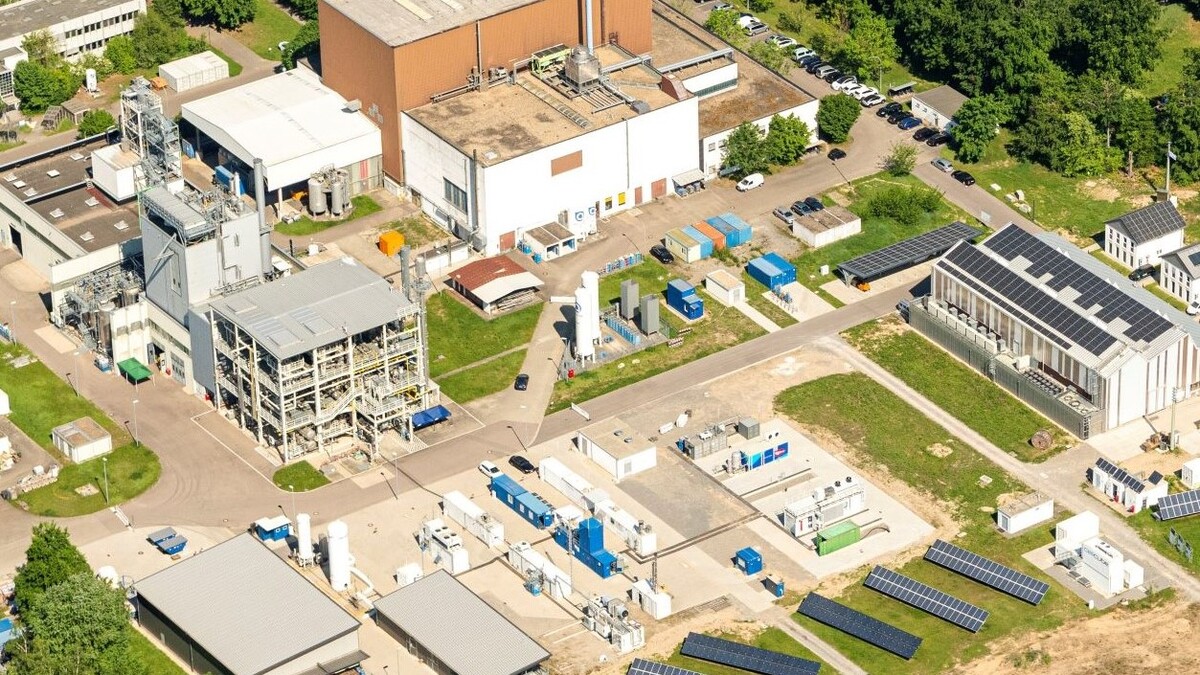
Energy Lab 2.0: Test Field for Future Energy Systems
Europe’s largest infrastructure for renewable energy focuses on the intelligent networking of environmentally compatible options to generate, store, and supply energy. At Hannover Messe, researchers will provide information on the following topics in particular.
Europe’s largest infrastructure for renewable energy focuses on the intelligent networking of environmentally compatible options to generate, store, and supply energy. At Hannover Messe, researchers will provide information on the following topics in particular.
Power-to-X: Methanation and E-fuels
For the energy transition to be successful, the renewable power sector must be coupled with other energy sectors. In the area of chemical energy carriers, such as fuels and combustibles, this can be achieved using power-to-X approaches (P2X). In this case, synthetic chemical energy carriers are produced from hydrogen and CO2. If hydrogen is produced by electrolysis with green electricity and CO2 comes from a non-fossil source, the P2X products are nearly CO2-neutral. Research at the Energy Lab 2.0 covers the correspond¬ing plants. A Power-to-Liquid container produces so-called e-fuels, the Power-to-Gas plant generates climate-neutral methane for later power production by a gas turbine.
DeepStor: Generating and Storing Geothermal Heat throughout the Year
KIT’s Campus North is located in the geothermally relevant Upper Rhine Graben and, hence, possesses great potential for sustainable heat supply. Within the DeepStor project, researchers test a high-temperature aquifer storage system that is loaded in summer and unloaded in winter. The experimental setup allows for the execution of experiments to load and unload the storage system as well as for the investigation of the associated thermal, hydraulic, chemical, and mechanical processes in the thermal water cycle. Having demonstrated the feasibility, it is planned to integrate for research a high-temperature aquifer storage system in the existing heat grid of KIT’s Campus North.
Hannover Messe 2022 | Hanover Fair 2022
Energy Solutions: From May 30 to June 2, 2022, KIT will present selected highlights from the technological development.
Energy Transition and Circular Economy
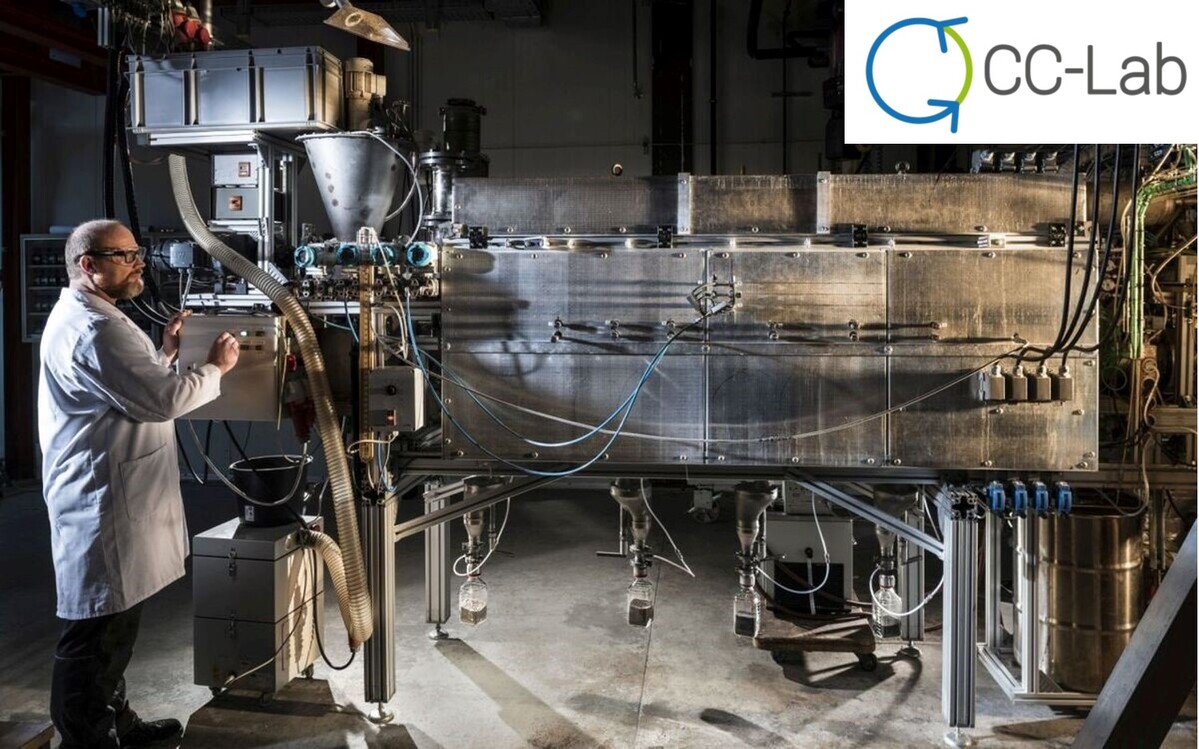
CarbonCycleLab
The CarbonCycleLab covers the complete process chain of the future carbon cycle: From residues and waste materials to basic chemical substances produced on their basis that will replace fossil fuels in chemical industry. The CarbonCycleLab combines the energy transition with circular economy and thus contributes to making future economy resource-efficient, climate-neutral, and competitive.
From a Climate-damaging Greenhouse Gas to an Economically Viable Material
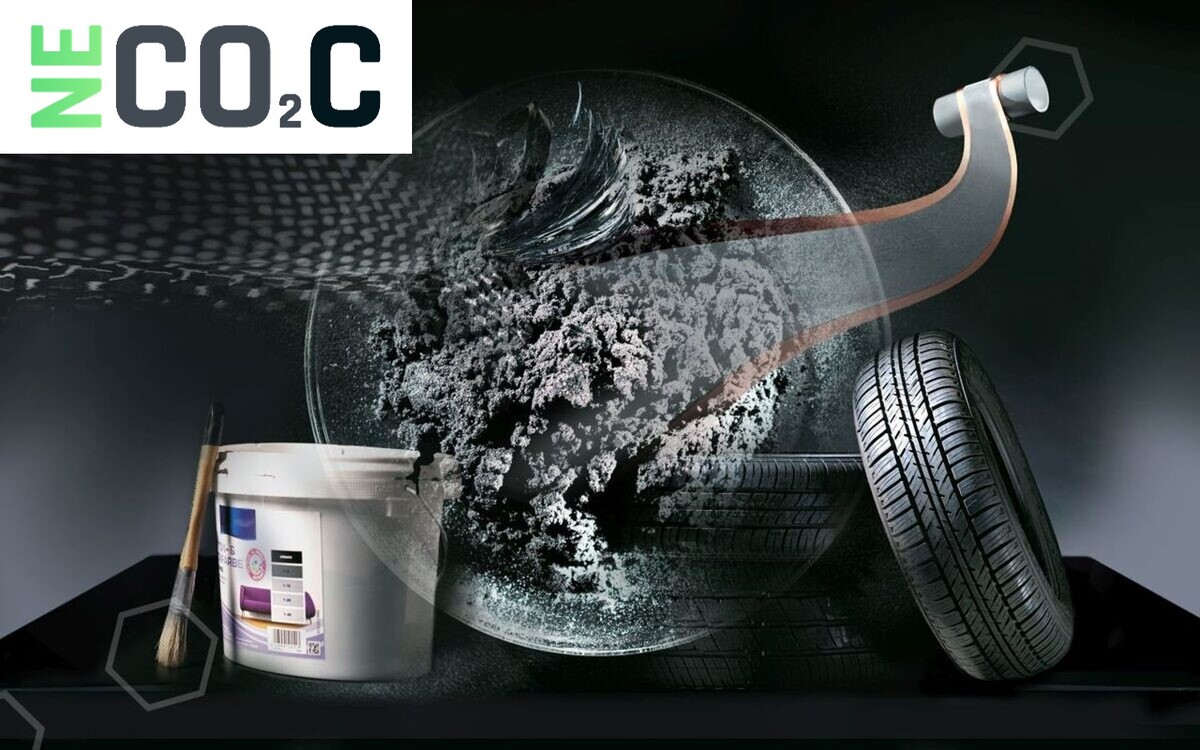
NECOC – Negative Emissions by Separating Atmospheric CO2 into Economically Viable Carbon Black and Oxygen
A consortium of KIT institutes and industrial companies has developed an integrated process to achieve negative emissions. Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is decomposed into elemental carbon (carbon black, C) and oxygen (O2). The solid carbon in the form of microgranular powder is separated and then, as a high-priced educt, used in rubber, construction, or electrical industries.
Towards Competitive Renewable Fuels
KIT’s startup ICODOS has developed a technology that efficiently combines carbon dioxide separation and methanol synthesis and, hence, contributes to making renewable fuels competitive. Initial implementation will concentrate on biogas. However, it is planned to also use the technology for other CO2 point sources in cement industry, for instance. A pilot plant is under construction and will be integrated in KIT’s Energy Lab 2.0.
Further information
How do we close the carbon cycle in the circular economy?
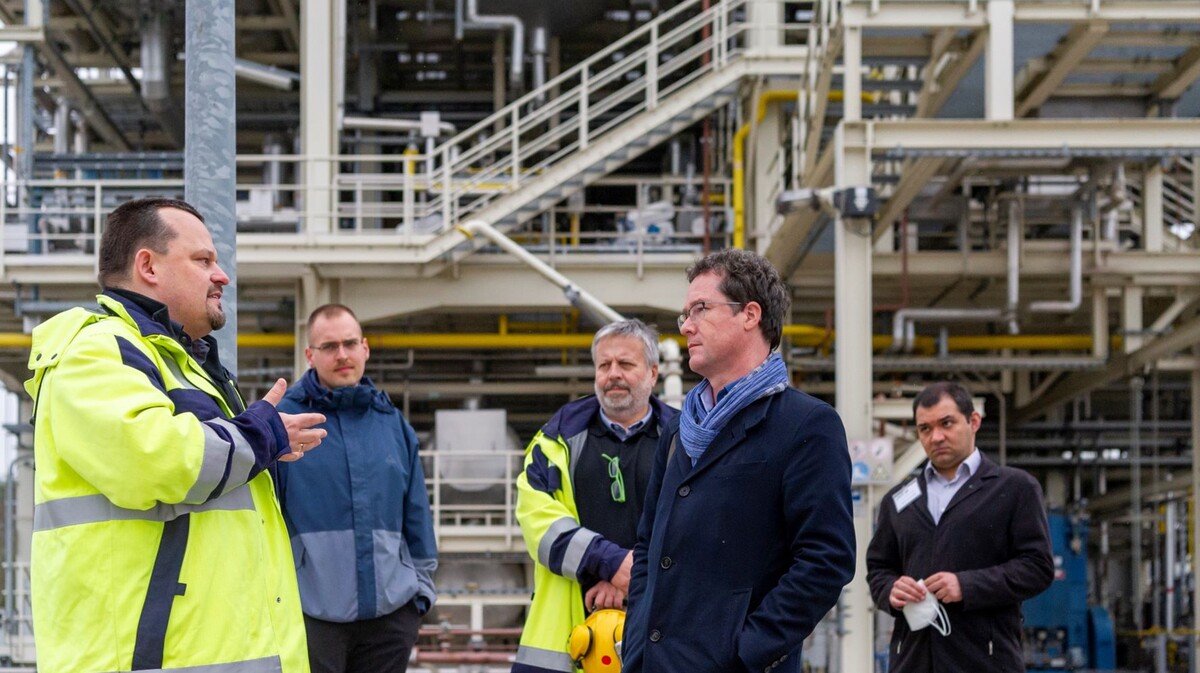
Mr. Harald Ebner, Member of the German Parliament and Chairman of the Committee on the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection visited KIT on March 31, 2022. In a discussion with scientists, Mr. Ebner informed himself, on the current context of the Ukraine crisis, how the dependence on fossil raw materials, such as oil, natural gas, and coal, can be overcome quickly.
On the one hand, this can be achieved by using biomass and carbon dioxide as a carbon source in industrial production processes, since today's industrial value networks are almost entirely based on fossil carbon. On the other hand, the carbon cycle must be closed within the framework of a circular economy. KIT is researching the technologies required for this:
- At the Carbon Cycle Lab we are researching the chemical recycling of mixed plastic waste;
- At the bioliq® pilot plant, we are researching how fuels and chemical feedstocks can be efficiently produced from residual biomass;
- At the Energy Lab 2.0, we are researching various technologies for storing renewable electricity in the form of chemical energy carriers.
The extraordinary importance of plastics recycling is due to the following reasons: Few of today's products are made of only one type of plastic, which could be recycled by simple mechanical collection by type. The processing of multiple types of plastics with additives for specific functions in laptops, cars, packaging and construction plastics makes it necessary to separate them back into their basic chemical building blocks. Pyrolysis is a chemical recycling process that converts plastic waste into gaseous, liquid and solid products in an inert atmosphere and at elevated temperature to replace fossil petrochemical feedstocks. So far, only a very small part of the world's annual plastic production (> 350 million tons) is actually recycled, therefore these techniques are crucial for a Circular Carbon Economy to implement the European Green Deal and become climate neutral by 2050.
Citizen Dialogue | School Labs - Kids' University - Boys & Girls Day - Career Orientation Traineeship (BOGY & BORS)

We offer girls from 8th grade onwards exciting insights into our work & labs: Fuels from air & green energy @IMVT, H2 a sustainable energy storage @ITCP/IKFT, Battery empty?! @BTC
more@Girls' Day Radar
...is an authentic place of learning & teaching. It provides insights into current research topics of superconductor technology & energy supply.
KIT School Lab Energy website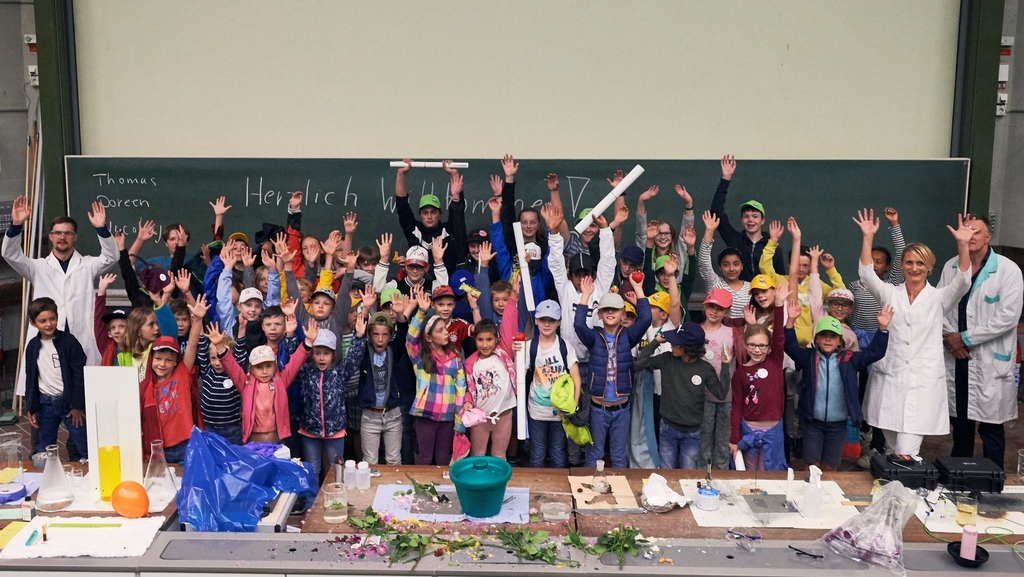
Lectures and interactive workshops during the summer vacations for children aged 7 to 14 at the KIT Children's University Campus. >>> website

The pupils (9th grade) gain their first practical experience in the school internship and thereby get an insight into their possible dream job.
more
The school lab for pupils (10th grade upwards) offers various practical courses as full-day internships, 9 am to 4 pm, including a guided tour through the institutes research labs.
moreCongress "Energy Efficiency Research for Industry and Business"

Research and development opens the way for a successful energy transition in industry and makes it possible to achieve climate targets in the long term. Thus, the Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Action (BMWK) supports corresponding projects with its energy research program. In this spirit, the "Energy Efficiency Research for Industry and Business" congress will be held at the Tagungswerk Berlin from May 17 to 18, 2022.
- Learn more about successes and trends in industrial energy research
- Contribute to future energy research funding with your own experience
As an event of the Energy Research Networks, the congress is organized by the recently completed accompanying research for industry and commerce (EE4InG with partners from ETA solutions, IREES, KIT, TU Darmstadt) and the PtJ on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Action.